With the rapid growth in bandwidth demands, campus LANs, building backbones, and data center backbones are exploring the adoption of ribbon fiber jumpers as a new solution. Ribbon fiber jumpers, with their unique advantages, have shown broad application prospects in these areas. This article primarily focuses on the advantages, application areas, and significant differences between ribbon fiber jumpers and other types of fiber jumpers.

Definition of Ribbon Fiber Jumpers

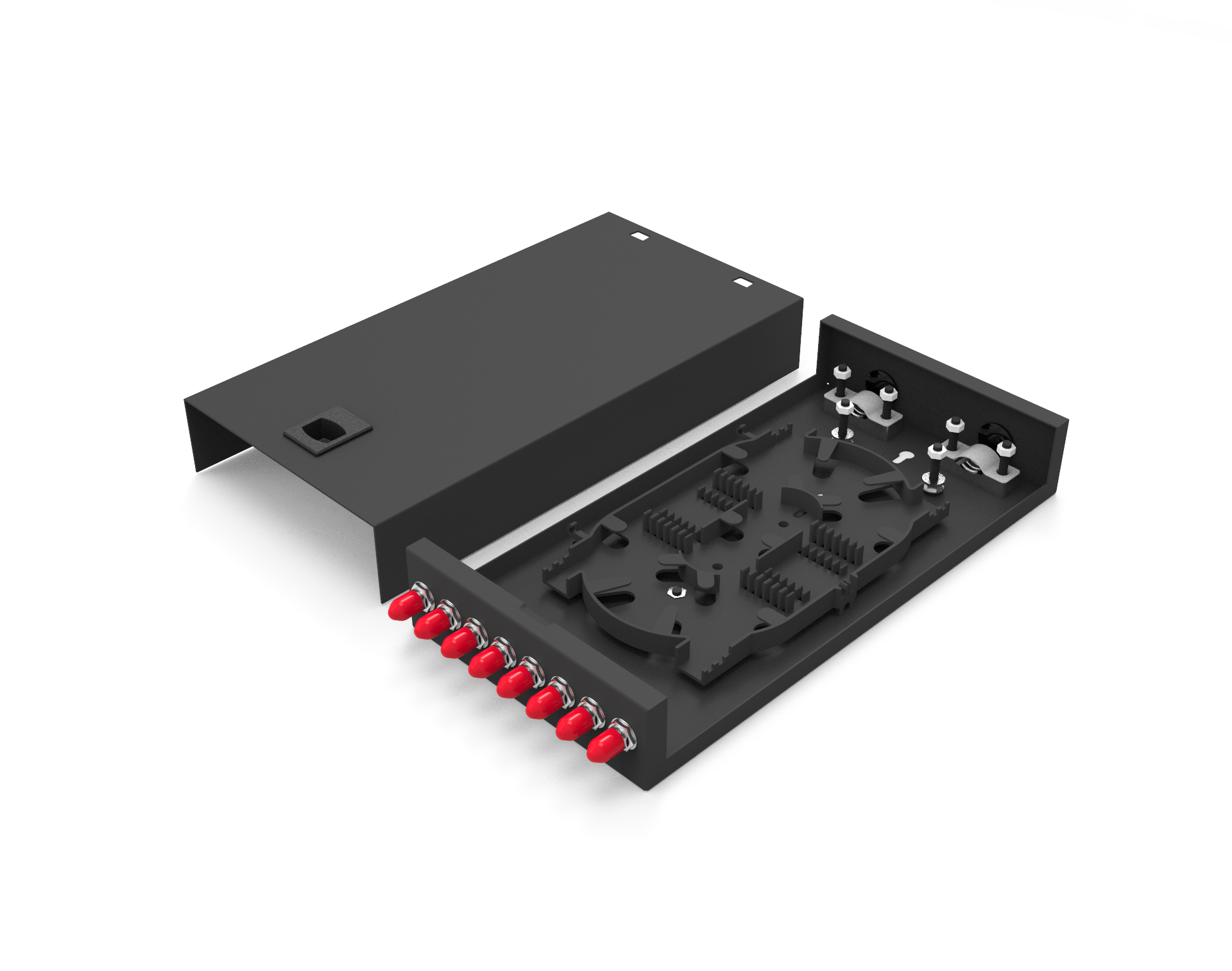
Characteristics and Advantages of Ribbon Fiber Jumpers
Types of Ribbon Fiber Jumpers
Differences Between Ribbon Fiber Jumpers and Bundle Fiber Jumpers

Upon closer inspection, the two also differ significantly in structure. Ribbon fiber jumpers are primarily composed of ribbon fibers, arranged in a highly organized manner; in contrast, bundle fiber jumpers are mainly comprised of 0.9mm jacketed cables, with each fiber relatively independent and lacking a fixed arrangement order.

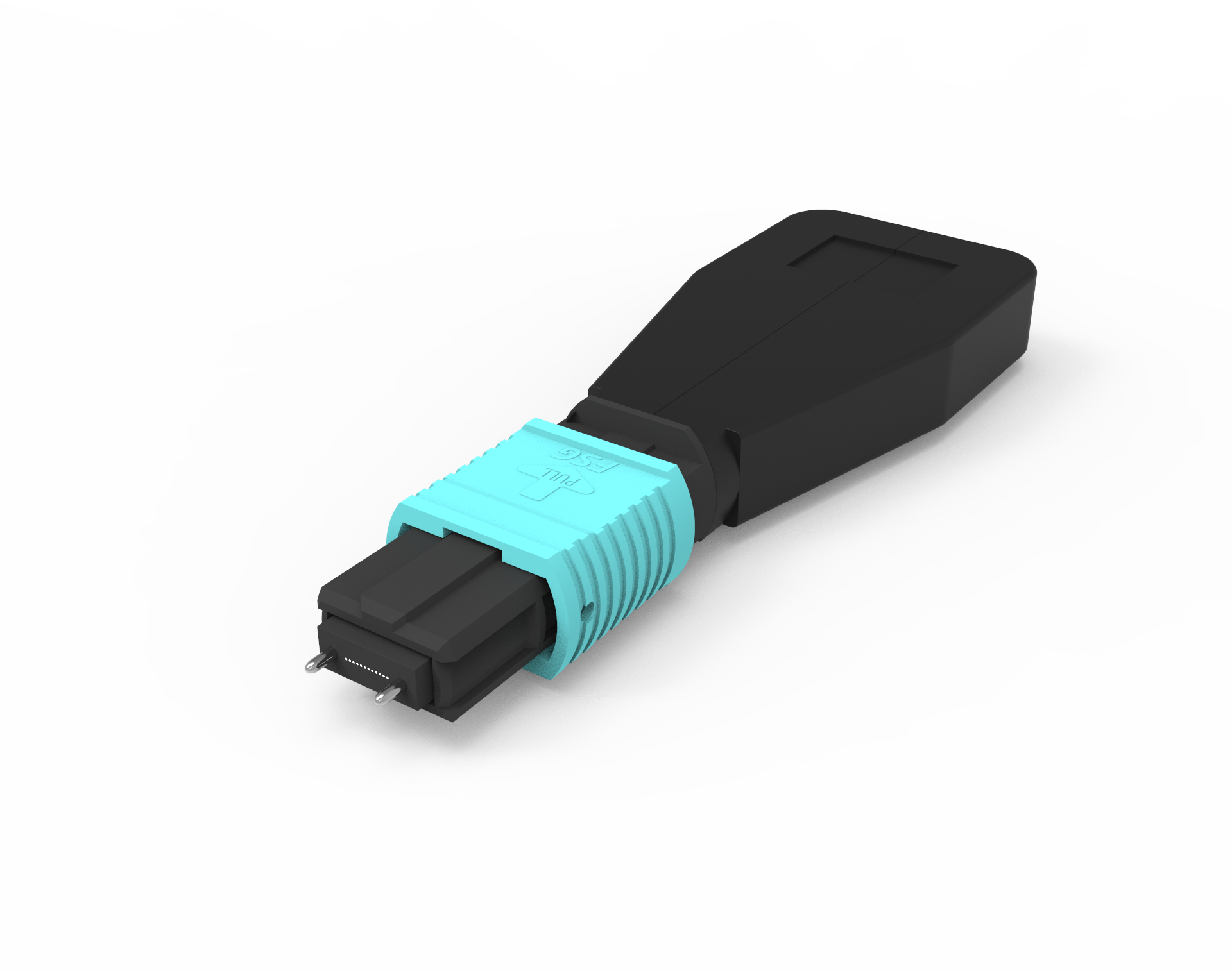
Ribbon fiber jumpers, as the name suggests, resemble an elegant ribbon, composed of tightly arranged 8, 12, or 24 fibers, neatly aligned like a queue. This design endows ribbon fiber jumpers with outstanding fiber density characteristics, enabling efficient utilization of every inch of space within limited areas, thus significantly saving space. For upstream applications with urgent demands for high-density fibers, ribbon fiber jumpers undoubtedly become an indispensable solution. Its emergence not only enhances the efficiency of fiber deployment but also propels further development in data transmission technology.

One significant advantage of ribbon fiber jumpers lies in their outstanding space-saving capability. Compared to traditional fiber jumpers, ribbon fiber jumpers can reduce space occupancy by up to 45% and increase fiber tray capacity by threefold. This characteristic maximizes fiber deployment within limited spaces, meeting the growing demand for fiber connections.
Furthermore, ribbon fiber jumpers offer significant cost and time savings. They allow the splicing of 12 fibers at once, greatly reducing labor time and costs for fiber connections. Additionally, ribbon fiber jumpers can integrate more fibers into smaller diameter jumpers, meeting the demands of high-density, high-bandwidth applications and providing a more efficient and cost-effective solution for data transmission.


Ribbon fiber jumpers can be categorized into flat ribbon fiber jumpers and round ribbon fiber jumpers based on their external design differences. The main distinction between the two lies in their shapes, but regardless of the type, the parallel fibers are arranged side by side to ensure fiber density and stability.
In terms of fiber types, ribbon fiber jumpers are divided into single-mode ribbon fiber jumpers and multimode ribbon fiber jumpers. These two types of jumpers also differ in their sheath options, with choices between flame-retardant and non-flame-retardant. Typically, non-flame-retardant sheathed fiber jumpers are more suitable for outdoor environments due to their better weather resistance. Flame-retardant sheathed fiber jumpers, on the other hand, are mostly used for indoor applications to effectively reduce the risk of fire spread under specific conditions, such as during a fire outbreak. This design ensures that ribbon fiber jumpers can perform optimally in various usage scenarios.

Ribbon fiber jumpers and bundle fiber jumpers exhibit significant differences in appearance and structure. Firstly, in terms of appearance, ribbon fiber jumpers utilize flat ribbon-shaped fiber cables, allowing for a more compact fiber arrangement, whereas bundle fiber jumpers typically use round-shaped bundle fiber cables, appearing looser in structure.

Upon closer inspection, the two also differ significantly in structure. Ribbon fiber jumpers are primarily composed of ribbon fibers, arranged in a highly organized manner; in contrast, bundle fiber jumpers are mainly comprised of 0.9mm jacketed cables, with each fiber relatively independent and lacking a fixed arrangement order.
Regarding fiber arrangement, ribbon fiber jumpers demonstrate their uniqueness. The fibers inside are neatly arranged in a specific color sequence, presenting a ribbon-like feature, and this arrangement is relatively fixed; whereas bundle fiber jumpers differ in this aspect, with fibers inside lacking a specific arrangement pattern, each maintaining a relative independence.



































































 Ann
Ann












