With the rapid development of modern communication technology, the demand for 40G/100G network cabling in data centers is growing day by day. The widespread use of high-density MPO fiber connectors and Patch Cord is becoming increasingly common to meet the requirements of high-speed transmission and large-capacity data storage.
1.Introduction to MPO Fiber Patch Cord
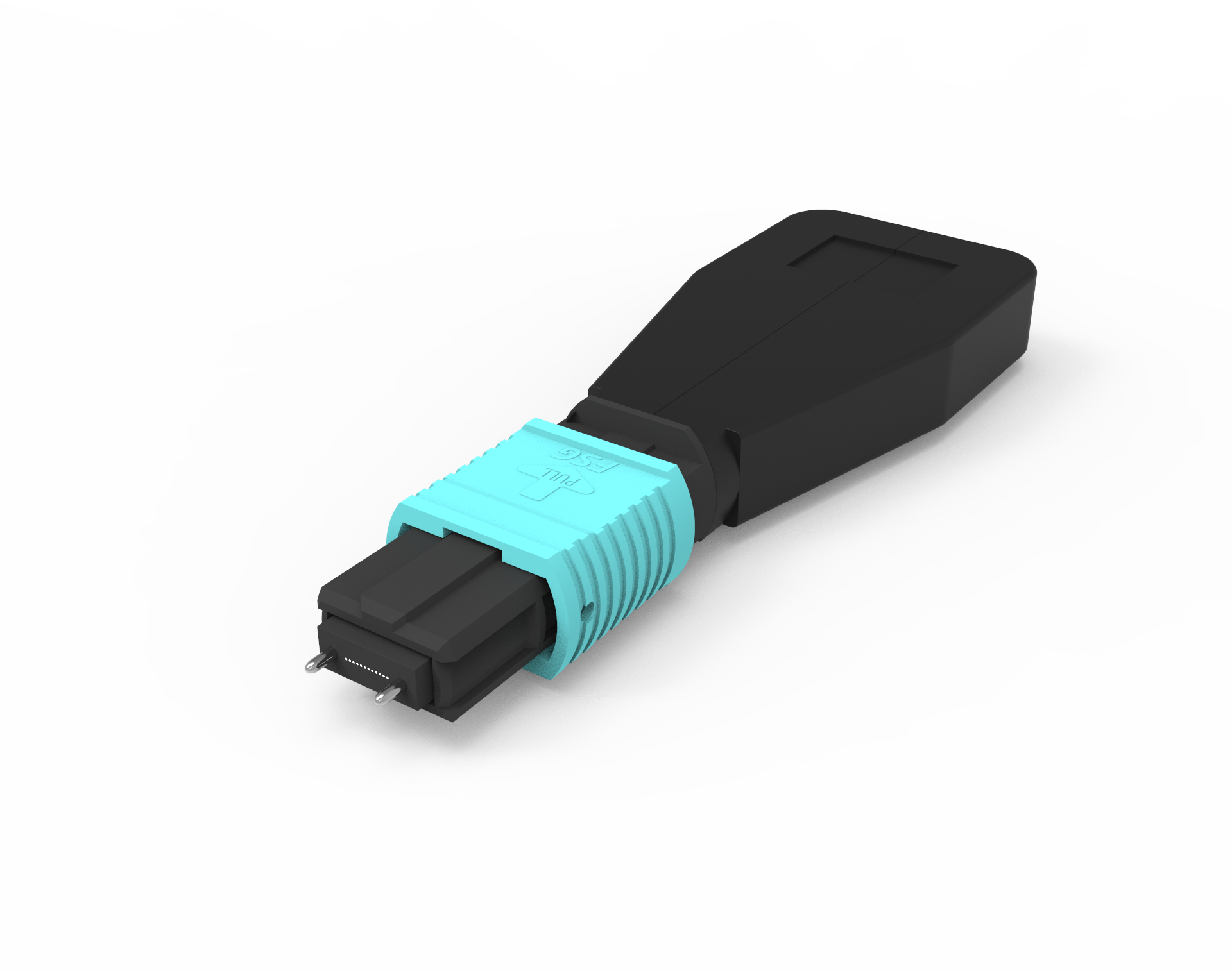
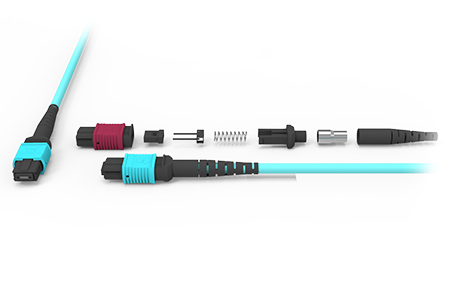
MPO fiber Patch Cord are meticulously crafted by combining advanced hot-pluggable MPO connectors with multi-mode/single-mode optical cables. The key component—the MPO fiber connector—boasts a sophisticated internal structure comprising optical fibers, sheath, coupling components, metal rings, pins, and dust caps, among other fine elements. The design of its pins is particularly unique, available in two forms: male and female.
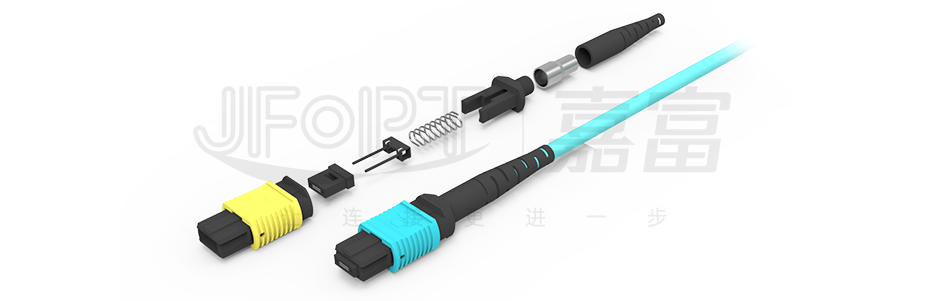
The male connector features two PIN pins, a design absent in the female connector. With its low insertion loss, excellent interchangeability and plugability, and a rich number of fiber cores, MPO fiber jumpers have become the ideal choice in high-density integrated fiber cabling scenarios.
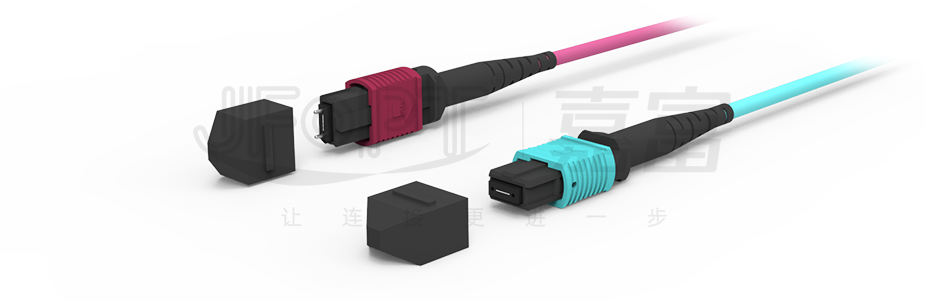
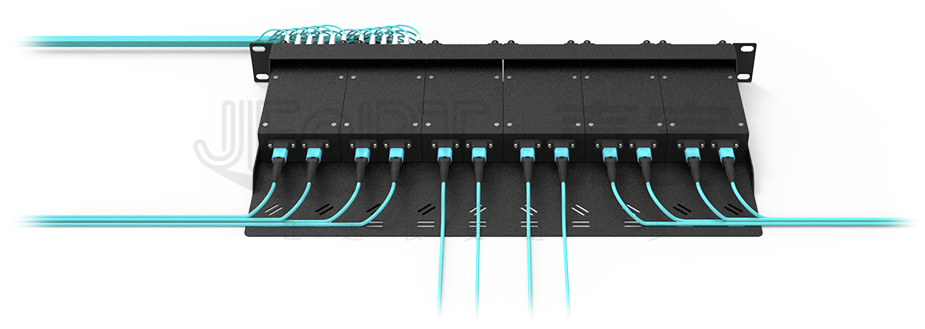
MPO Patch Cord find wide-ranging applications across various network environments, including fiber optic communication systems, cable television networks, telecommunications networks, local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), and more. They play a crucial role in scenarios such as internal wiring in communication base stations, wiring in distribution boxes, and optical link interconnections in active optical equipment.
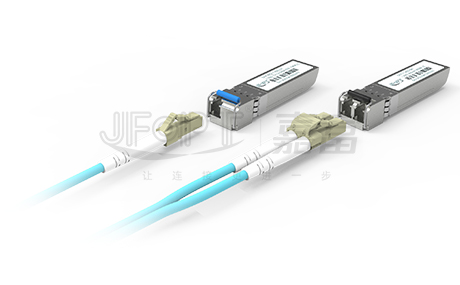
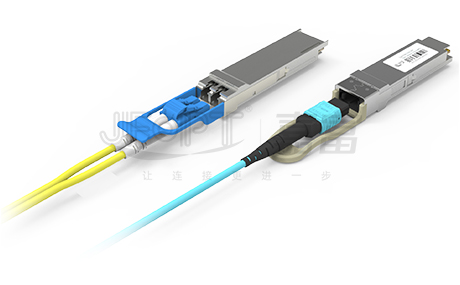
In practical applications, MPO Patch Cord often work in tandem with high-speed optical modules of 40G or higher. For instance, optical modules like 40G QSFP+ SR4, eSR4, PSM4, and 100G QSFP28 SR4, PSM4 utilize parallel transmission with four transmitting and four receiving channels. Thus, to ensure smooth optical link connections, at least an 8-fiber MPO fiber Patch Cord is required.
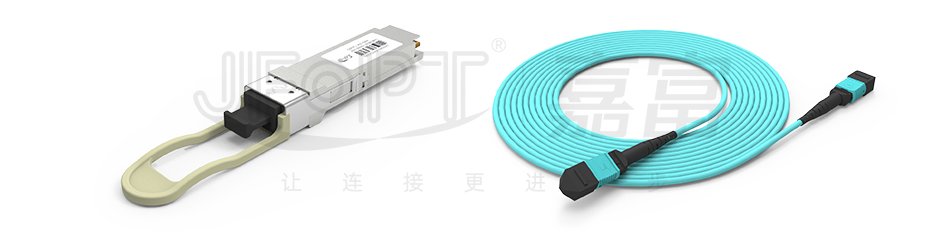
It's worth noting that optical modules such as 40G QSFP+ SR4 and 40G QSFP+ PSM4 typically employ a 12-fiber MPO interface. This is because the channel specifications remain consistent during the production of QSFP+ optical modules, where channels 1 and 12, channels 2 and 11, channels 3 and 10, and channels 4 and 9 respectively form four pairs of transmitting and receiving channels. The four middle channels are not utilized. Each pair of transmitting and receiving channels operates at 10G transmission, collectively achieving a transmission speed of 40G.
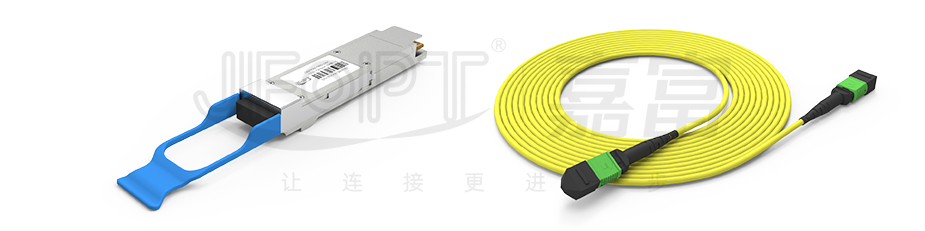
Apart from 40G/100G optical modules, 12-fiber MPO jumpers can also be used for 100G CFP4 SR4 optical modules. For optical modules like 100G CFP2 SR10 and 100G CFP SR10, however, 24-fiber MPO jumpers are generally preferred.
3.Classification of MPO Fiber Patch Cord
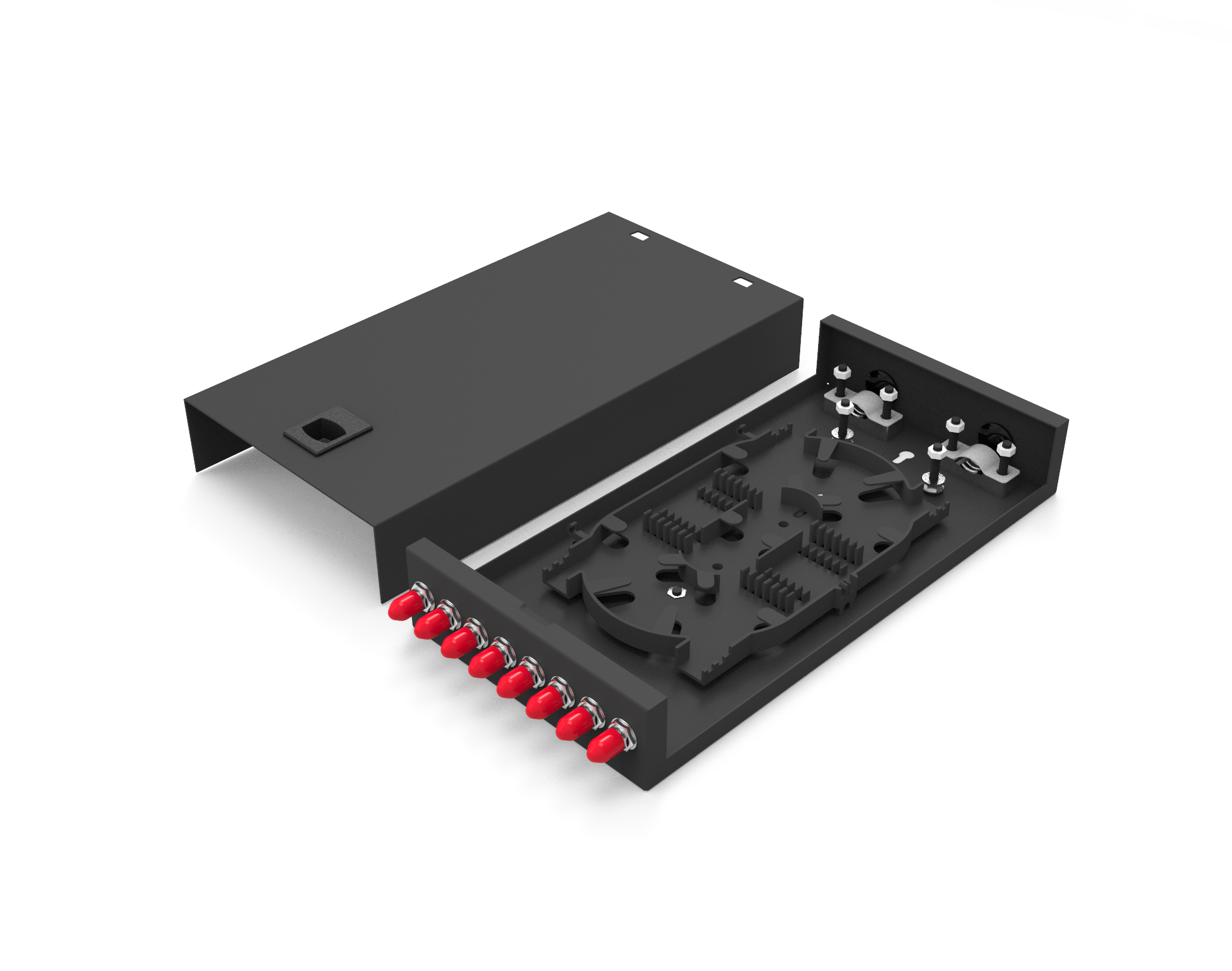
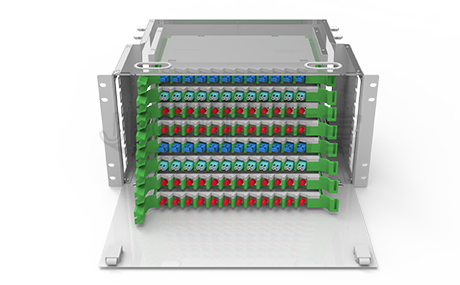
MPO fiber jumpers, efficient and multifunctional fiber optic connectivity tools, can be classified based on different standards. From the perspective of connector types, they can be divided into two main categories: MPO trunk fiber jumpers and MPO branch fiber jumpers. These two types of jumpers have their own characteristics in structural design and application scenarios, meeting the needs of different network cabling.

Additionally, MPO Patch Cord can also be classified based on the number of fiber cores. Currently, common core counts available in the market include 8 cores, 12 cores, 24 cores, 36 cores, 48 cores, and 72 cores, among others.
4.Classification of MPO Fiber Patch Cord by Polarity
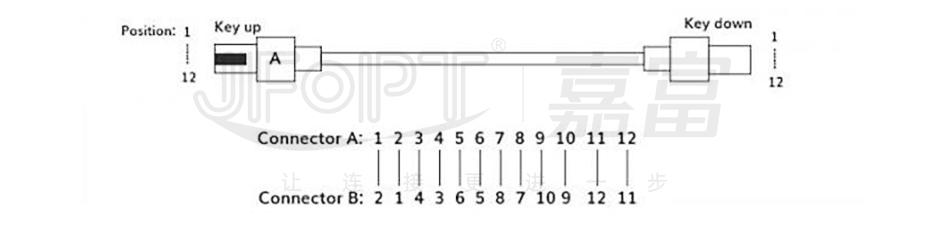
1) Type A (Straight-Through): MPO Patch Cord have a unique design feature. The arrangement of fiber cores at both ends remains identical, meaning the first fiber core at one end corresponds to the first fiber core at the other end, and similarly, the twelfth fiber core at one end corresponds to the twelfth fiber core at the other end. It's worth noting that the orientation of the Key on both ends of this type of patch cord is opposite; one end is Key up, while the other end is Key down.
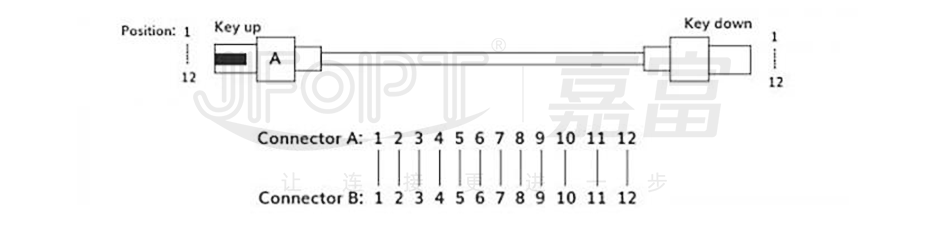
2) Type B (Cross-over): MPO Patch Cord are ingeniously designed. The arrangement of fiber cores at both ends of this type of jumper presents a reverse pattern, where the first fiber core at one end corresponds to the twelfth fiber core at the other end, and vice versa. In terms of Key orientation, the direction of both ends is consistent, meaning Key up corresponds to Key up, and Key down corresponds to Key down.
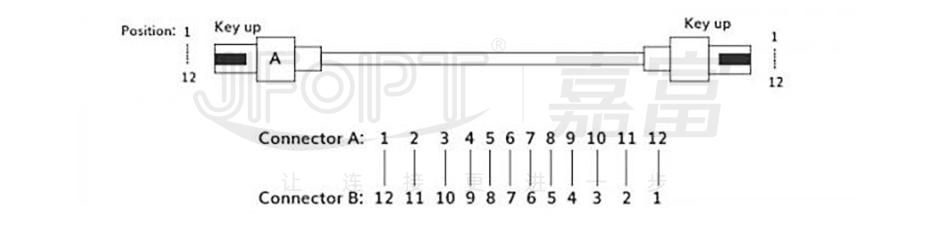
3) Type C (Pair-wise Cross-over): MPO Patch Cord employ a unique arrangement of fiber cores. In the design of this type of jumper, adjacent pairs of fiber cores are crossed over. Specifically, the first fiber core at one end corresponds to the second fiber core at the other end, while the twelfth fiber core at one end corresponds to the eleventh fiber core at the other end. Additionally, the Key orientation at both ends is in opposite states, where Key up corresponds to Key down.
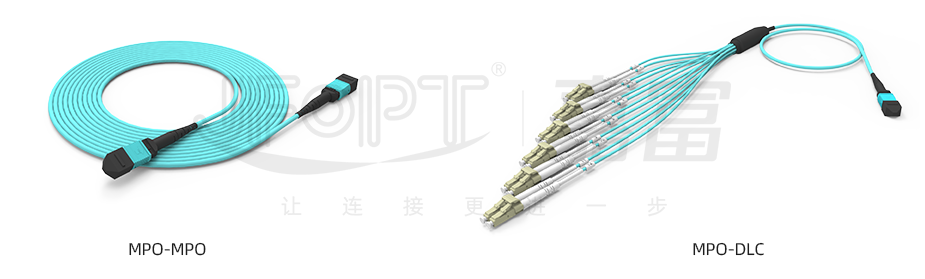
5.Types of MPO Fiber Patch Cord
6.Precautions for Using MPO Fiber Patch Cord
1) Ensure that MPO Patch Cord remain smooth, avoiding knots, bends, twists, or being stretched or squeezed to ensure normal operation and prolong their lifespan.
2) Regularly inspect the fiber jumpers for signs of folds or connector damage. Once an issue is detected, address it promptly to avoid affecting optical signal transmission.
3) Properly label wiring infrastructure, including patch panels, to clearly identify the location and purpose of each MPO Patch Cord, enhancing management and maintenance efficiency.
4) When bundling MPO Patch Cord, avoid excessive tightness to prevent unnecessary pressure and damage, which could affect the performance and lifespan of the fiber patch cord.











































































 Ann
Ann












