Before discussing the signal splitting construction of FTTH networks, it is essential to understand the different types of optical splitters. The two most commonly used optical splitters are PLC (Planar Lightwave Circuit) splitters and FBT (Fused Biconical Taper) splitters. Below are the main differences between them.
| Parameters | PLC optical splitter | FBT optical splitter |
| Wavelength range | 1260-1650 nm | Single/Dual/Triple Window |
| Split ratio | Even distribution | Even or uneven distribution |
| Volume | Small | Large volume when multi-path splitting |
| Wavelength sensitivity | Low | High |
| Price | Higher | Lower |
With the widespread adoption of FTTH networks, PLC optical splitters have become a popular choice in FTTH applications due to their high splitting ratios and uniform signal distribution, effectively meeting the needs of more users.


Secondary splitting refers to achieving signal splitting between the OLT (Optical Line Terminal) and the ONU (Optical Network Unit) through a cascade of two sets of optical splitters. This method includes two splitting points: the primary splitting point and the secondary splitting point.
The primary splitting point is usually located near the central office and typically uses a 1×4 optical splitter. The secondary splitting point is generally located closer to the user, such as in a hallway, and utilizes multiple optical splitters, often 1×8 splitters.
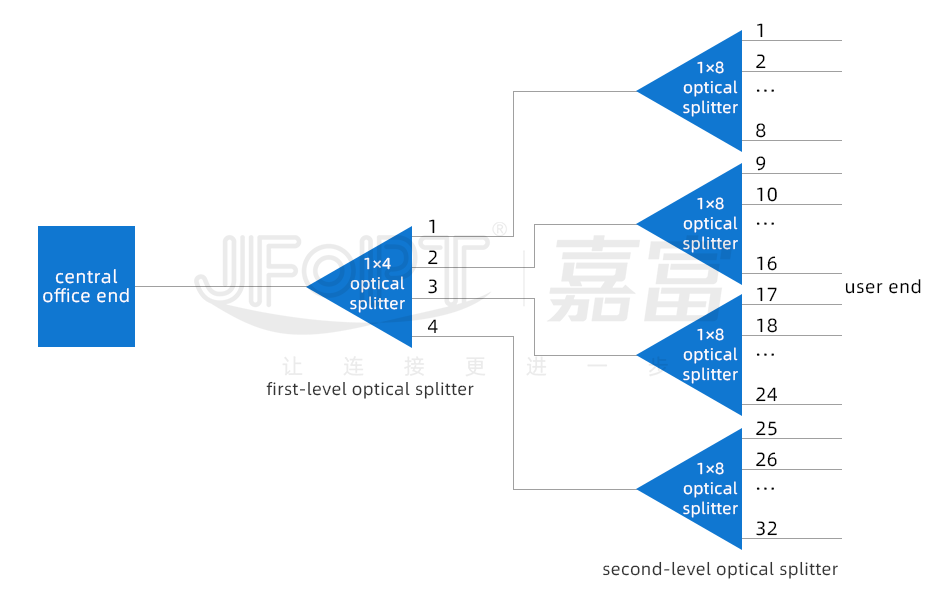
The primary splitting method (centralized arrangement of optical splitters) offers high flexibility, low operational costs, and ease of maintenance. In contrast, the secondary splitting method (cascaded arrangement of optical splitters) is characterized by a quicker return on investment and lower initial capital costs. Consequently, the primary splitting method is typically suited for densely populated urban or town areas, while the secondary splitting method is more appropriate for sparsely populated rural regions.
In PON networks, commonly used optical splitters include 1:N(N=2~64)and 2:N(N=2~64) types, with "N" representing the number of output ports. Different splitting ratios of optical splitters serve various roles in FTTH networks.



































































 Ann
Ann












