With the continuous growth of user numbers, fiber optic cabling is becoming increasingly complex. In this context, how to efficiently utilize the space in transmission and data rooms and achieve standardized management of cables in the room has become increasingly crucial. The Optical Fiber Distribution Box (ODB), as the core equipment in the optical transmission system, plays a pivotal role.
The ODB is typically placed in optical communication rooms or racks, with its main responsibility being the management of fiber optic terminals and the implementation of distribution functions. The introduction of this equipment not only provides installation personnel with more diverse functional options but also injects new vitality into the flexibility of cabling. By using the Optical Fiber Distribution Box, installation personnel can more efficiently manage fiber optic cables and ensure the stable operation of the entire optical transmission system.
There are various types of Optical Fiber Distribution Boxes, including rack-mounted, cabinet-mounted, and wall-mounted. Among them, rack-mounted Optical Fiber Distribution Boxes are particularly suitable for installation in 19-inch standard racks. The height configuration of these distribution boxes is flexible and variable, and different rack units (RU) heights such as 1U, 2U, or 4U can be chosen according to different connection requirements. Here, "U" stands for "Unit" and is used to represent the height of network equipment.
Specifically, the height of a 1U Optical Fiber Distribution Box is equivalent to 44.45mm (1.75 inches), making it very suitable for environments with limited space. The height of a 2U distribution box is 88.9mm (3.5 inches), providing more space and supporting more fiber optic connections. As for a 3U distribution box, its height is 133.35mm (5.25 inches), providing ample wiring space for large-scale fiber optic networks.
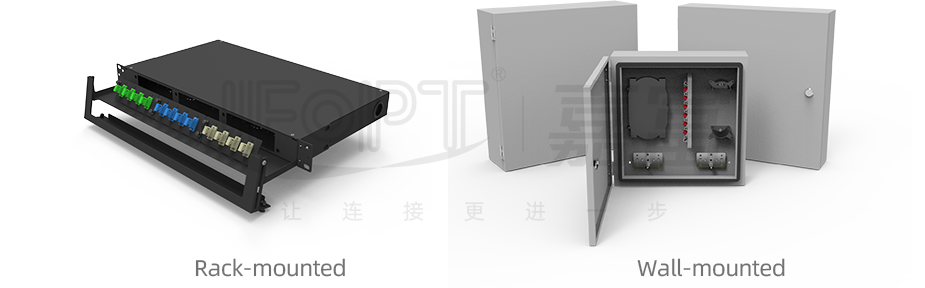

These size standards are not arbitrarily set but are determined by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) after rigorous research and testing. Therefore, whether it is a 1U, 2U, or 4U Optical Fiber Distribution Box, their main differences lie not only in height but also in the different numbers of fiber optic cores they can support. The choice of which type of distribution box to use needs to be comprehensively considered based on the actual network scale and wiring requirements.
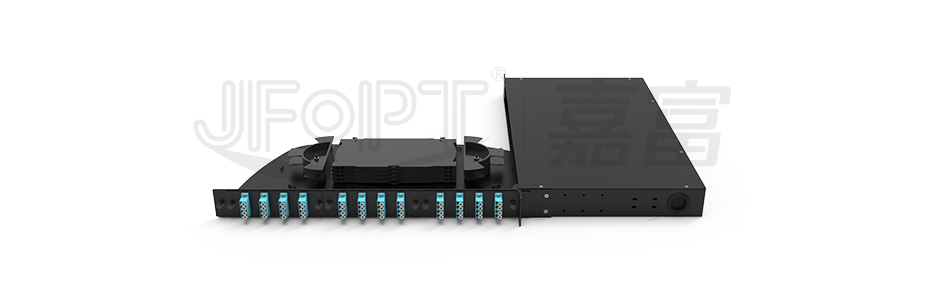
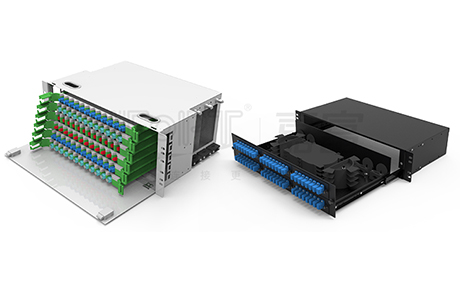
The design of rack-mounted fiber optic distribution boxes is diversified, and their installation methods can be divided into various types such as pull-out, rotary, and door latch. Each installation method has its own characteristics to adapt to different usage scenarios and requirements. Pull-out and rotary fiber optic distribution boxes are favored for their convenient use, but relatively speaking, their manufacturing costs may be slightly higher. On the other hand, distribution boxes with detachable enclosures, although more affordable in price, may lag behind in terms of operational convenience.


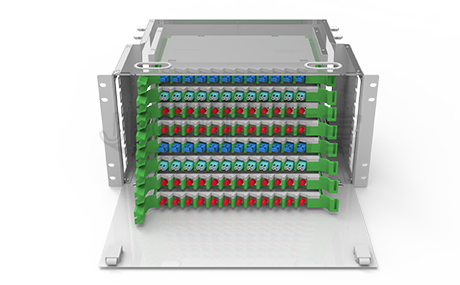
Among many types, drawer-type fiber optic distribution boxes have been widely used due to their unique advantages. So, what are the characteristics of pull-out fiber optic distribution boxes?
1.Modular tray design for convenient operation
The tray design of pull-out fiber optic distribution boxes is ingeniously crafted, featuring not only sliding functionality but also a locking mechanism. In practical use, users only need to gently pull, and the tray can smoothly slide out like a drawer, making the operation simple and convenient. Once the tray is pulled out, its locking function ensures that the tray stays stable in the desired position, providing users with great convenience for wiring operations. This design not only simplifies the wiring process but also significantly improves work efficiency, providing users with an unprecedentedly convenient experience.
2.Compact Structure, High-Density Wiring, Effective Space Saving
The design of pull-out fiber optic distribution boxes is intricately compact, capable of efficiently accommodating a large number of fiber optics and ports, significantly enhancing wiring density. This design ingeniously utilizes cabinet space, maximizing space utilization and effectively saving valuable cabinet resources. Whether in large-scale data centers or compact enterprise networks, it can easily meet the high-density fiber optic wiring requirements, providing a more efficient and flexible solution for network layout.
3.Reasonable Design, Efficient Cable Management
This fiber optic enclosure features a well-designed cable management system, with a front cable management rack capable of independently managing cable bundles, facilitating cable organization.

Pull-out fiber optic distribution boxes, with their outstanding flexibility and convenience, have become an ideal choice in the field of fiber optic communication. Their installation process is simple and fast, and maintenance and management are equally convenient, making the construction and operation of fiber optic networks more efficient. These distribution boxes can be used not only for jumper connections, fiber fusion, and fiber storage but also for easy management of high-density MTP cabling, meeting diverse application requirements.
In critical areas such as Main Distribution Areas (MDAs), Intermediate Distribution Areas (IDAs), or Horizontal Distribution Areas (HDAs) in data centers, pull-out fiber optic distribution boxes play an indispensable role. They can be equipped with pre-connected MPO/MTP adapter modules or MPO/MTP adapter front panels, enabling fast, stable interconnection and cross-connection between backbone optical cables and active equipment, providing strong support for fiber backbone connections and distribution management in data centers.
Overall, pull-out fiber optic distribution boxes, with their excellent performance and wide range of applications, have brought revolutionary changes to the construction and operation of fiber optic communication networks, making them indispensable equipment in the modern communication field.



























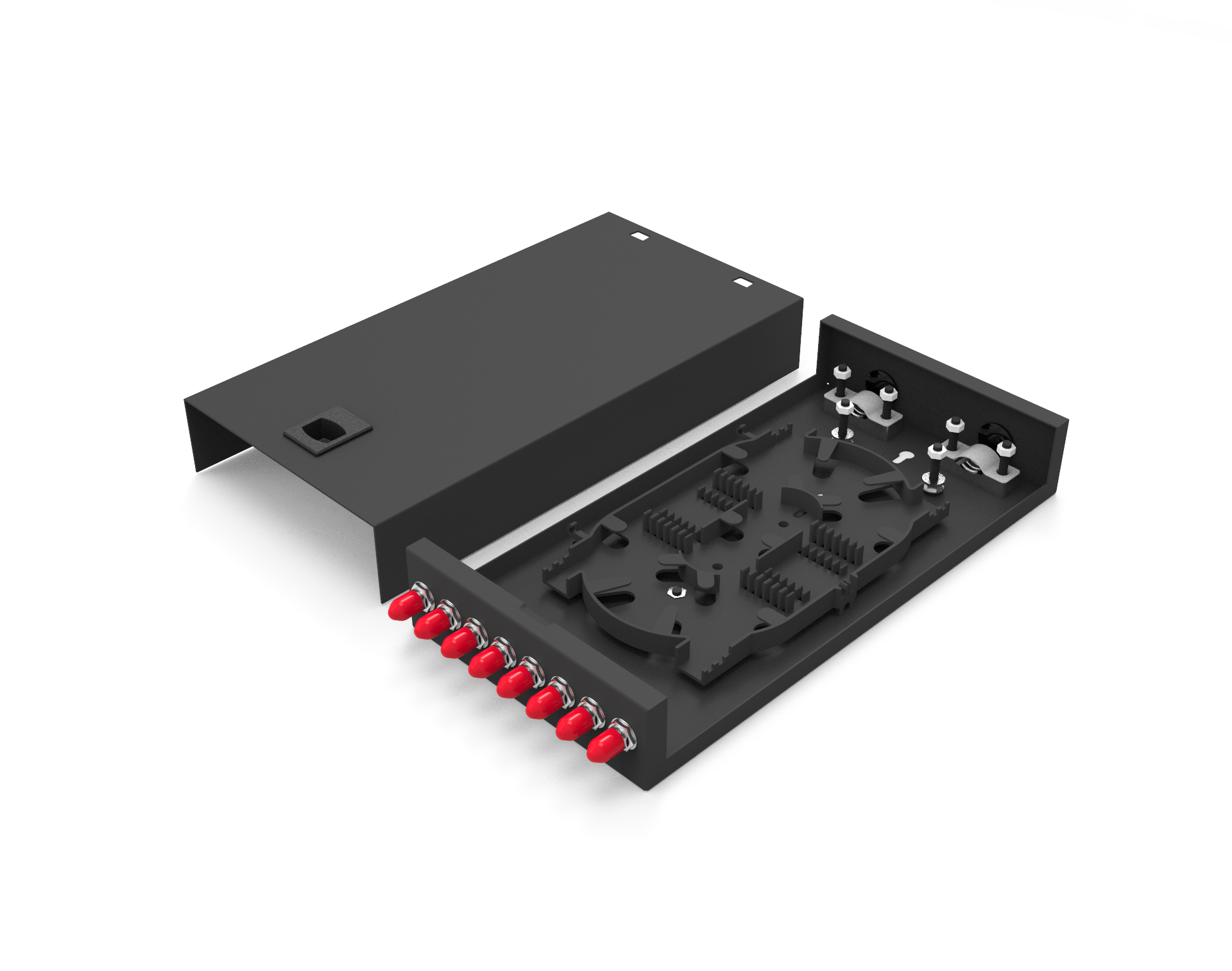








































 Ann
Ann












