With the rapid advancement of technology, the demand for networks is becoming increasingly vigorous. As a crucial medium for network transmission, optical fiber cables are becoming more and more popular. In diverse application scenarios, the types of optical fiber cables are also becoming more abundant, among which outdoor optical fiber cables and indoor optical fiber cables are particularly common. Although they both serve as mediums for transmitting optical signals, they exhibit many significant differences in practical use.

1. Differences in Environmental Adaptability
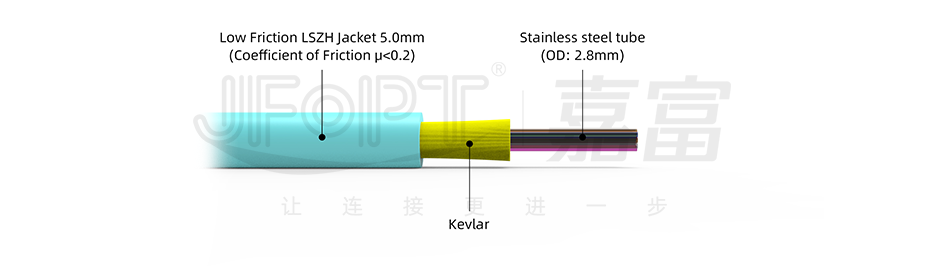
2. Differences in Optical Properties

Outdoor optical fiber cables, as reliable assistants in outdoor scenarios, are widely used in aerial, duct, and direct burial environments. To cope with natural challenges such as wind, rain, sunlight, temperature fluctuations, etc., they need to demonstrate outstanding environmental adaptability. Their outer sheath is made of high-strength polyethylene or polyvinyl chloride materials, with multiple characteristics such as waterproof, moisture-resistant, corrosion-resistant, and UV-resistant, ensuring stable operation even in harsh environments.
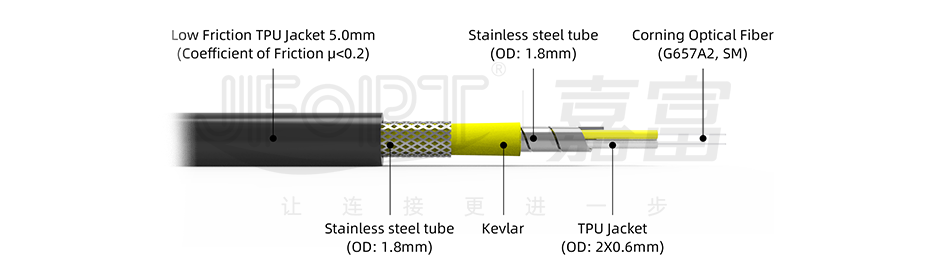

In contrast, indoor optical fiber cables primarily serve indoor environments such as data centers, office buildings, and residential buildings. Due to the relatively stable indoor environment, their outer sheath material focuses more on safety performance. Typically, they use low-smoke halogen-free flame-retardant materials, characterized by fire resistance, flame retardancy, low smoke, and non-toxicity. In the event of a fire, they can effectively reduce the generation of harmful gases and smoke, providing strong protection for personnel safety.

Outdoor optical fiber cables and indoor optical fiber cables also have their own strengths in terms of optical performance. Outdoor optical fiber cables need to meet stringent requirements for long-distance transmission, typically requiring low attenuation coefficients and high bandwidth. The attenuation coefficient, which represents the degree of signal loss during transmission, the lower the value, the farther the optical signal can travel. Bandwidth measures the transmission capacity of the fiber optic cable, with wider bandwidths capable of carrying larger amounts of data.
In comparison, the requirements for attenuation coefficients and bandwidth for indoor optical fiber cables are slightly more relaxed. After all, the transmission distances in indoor environments are relatively short, resulting in naturally smaller signal losses. Therefore, indoor optical fiber cables focus more on flexibility and ease of installation to meet the wiring demands within confined spaces.
3. Different Connection Methods

4. Considerations Regarding Cost
In summary, outdoor optical fiber cables and indoor optical fiber cables exhibit significant differences in environmental adaptability, optical properties, connection methods, and cost. Therefore, in practical applications, we need to carefully select the appropriate type of optical fiber cable based on specific scenarios and requirements to ensure stable and reliable network transmission. Such a choice will help improve communication quality and meet the needs of various application scenarios.
There are significant differences in the connection methods between outdoor optical fiber cables and indoor optical fiber cables. Outdoor optical fiber cables tend to use fusion splicing for connections. This method is known for its excellent connection quality and stability, ensuring minimal signal loss during transmission. However, fusion splicing requires specialized equipment and technical support, so it is typically performed by experienced professionals.
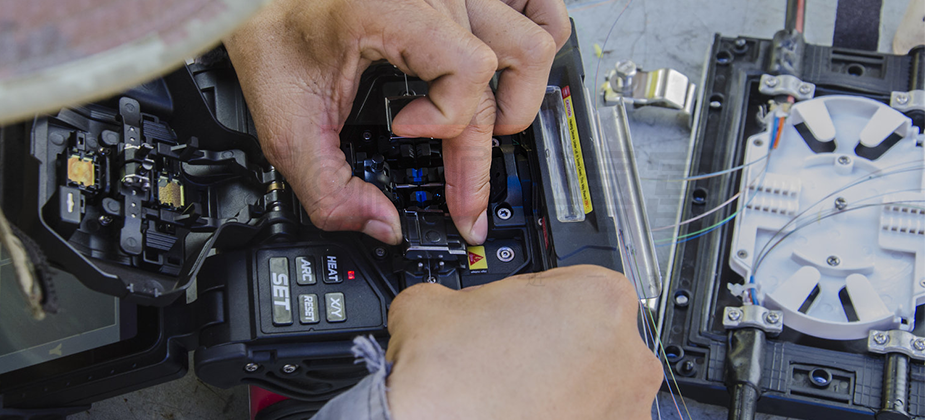


In contrast, the connection methods for indoor optical fiber cables are more flexible and diverse. They often use quick connectors or cold fusion for connections. Quick connectors do not require fusion splicing; they achieve fast connections of optical fiber cables mechanically, offering the advantages of simplicity and speed. Cold fusion, on the other hand, utilizes matching liquids to connect optical fiber cables, which is relatively simple to operate but may slightly lag behind fusion splicing in terms of connection quality and stability.

Considering the high requirements of outdoor optical fiber cables for environmental adaptability and optical properties, their production costs are often relatively high. Moreover, the installation and maintenance of outdoor optical fiber cables also require specialized equipment and technical support, which undoubtedly further increases their cost burden.
In contrast, the production costs of indoor optical fiber cables are relatively low, and their installation and maintenance processes are also simpler. This makes indoor optical fiber cables have a certain competitive advantage in terms of cost, making them the preferred solution for indoor wiring.
In summary, outdoor optical fiber cables and indoor optical fiber cables exhibit significant differences in environmental adaptability, optical properties, connection methods, and cost. Therefore, in practical applications, we need to carefully select the appropriate type of optical fiber cable based on specific scenarios and requirements to ensure stable and reliable network transmission. Such a choice will help improve communication quality and meet the needs of various application scenarios.



































































 Ann
Ann












