The current fiber patch cord market is indeed complex. For the same conventional 1-meter SC single-mode patch cord, its price can fluctuate significantly, ranging from one to over ten dollars. So, what exactly causes such a huge difference in fiber patch cord prices?
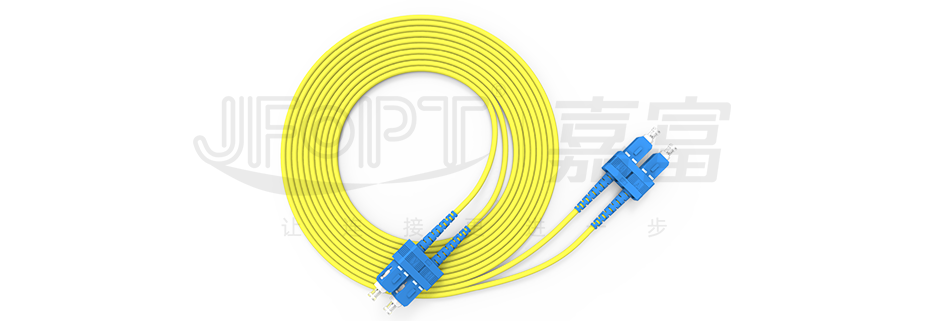

Fiber connector patch cords, with connector plugs at both ends of the cable, are designed to achieve flexible optical path connections. Those with plugs at only one end are referred to as pigtail cables.
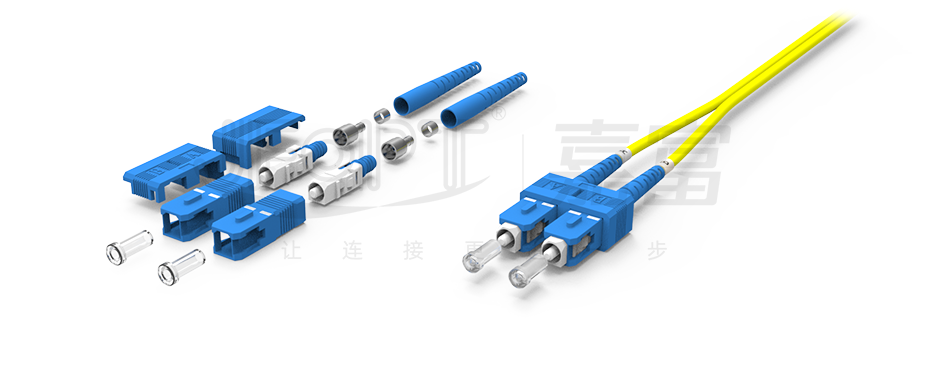
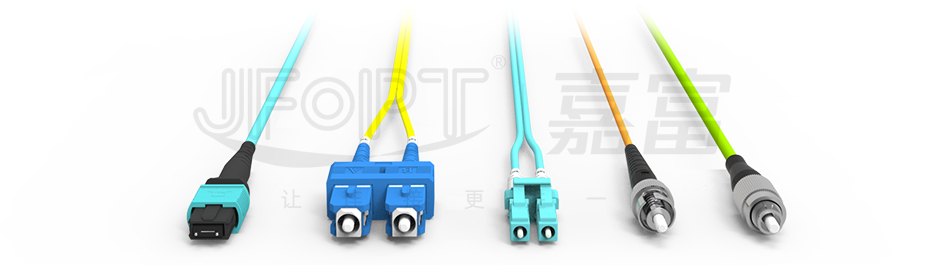
There are various types of connector heads for fiber connectors, including LC, FC, SC, ST, etc., while the end-face contact methods are divided into PC, UPC, and APC types. If the connectors at both ends of the patch cord are different, it is referred to as a conversion patch cord.
Against the backdrop of the country's vigorous promotion of 'optical over copper,' fiber optics have gradually entered thousands of households and become well-known to the public.
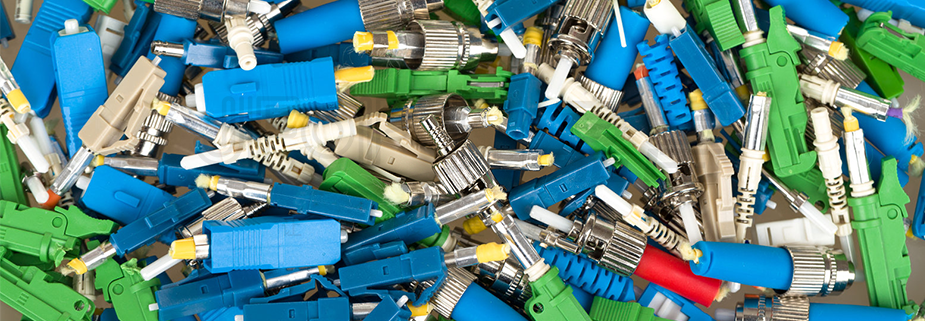
The popularity of fiber optics cannot be separated from fiber patch cords, which serve as crucial bridges. However, there are some makeshift workshops in the current market. In pursuit of exorbitant profits and cost reduction, they resort to using second-hand inserts and components to produce fiber patch cords. This undoubtedly poses great harm and risks to the high-speed and stable networks of fiber optics. To ensure the smooth operation of networks at high speeds, we must have a deep understanding and grasp of the standards and workmanship of the 'bridge,' namely fiber patch cords.

Therefore, when purchasing fiber patch cords, it is essential to choose products produced by reputable factories. These products typically adhere to stringent telecommunications-grade testing standards, ensuring reliable and stable product quality.

There are various types of connector heads for fiber connectors, including LC, FC, SC, ST, etc., while the end-face contact methods are divided into PC, UPC, and APC types. If the connectors at both ends of the patch cord are different, it is referred to as a conversion patch cord.

Against the backdrop of the country's vigorous promotion of 'optical over copper,' fiber optics have gradually entered thousands of households and become well-known to the public.
The popularity of fiber optics cannot be separated from fiber patch cords, which serve as crucial bridges. However, there are some makeshift workshops in the current market. In pursuit of exorbitant profits and cost reduction, they resort to using second-hand inserts and components to produce fiber patch cords. This undoubtedly poses great harm and risks to the high-speed and stable networks of fiber optics. To ensure the smooth operation of networks at high speeds, we must have a deep understanding and grasp of the standards and workmanship of the 'bridge,' namely fiber patch cords.

1. Regarding the sources of second-hand inserts and components:
These goods mainly come from two major channels. Firstly, some are scrapped inserts and components removed after prolonged use. Secondly, another portion comes from defective rework inventory directly removed by manufacturers during testing on the production line. As long as these products can achieve basic light transmission functionality, they are extensively used in the manufacturing of fiber patch cords to reduce costs and pursue higher profits.
2. In-depth Analysis of Hazards:
Severe Optical Path Contamination: Due to the use of scrapped materials or defective products, the interior of these fiber patch cords contains a large amount of dust and particles, severely contaminating the optical path and causing significant interference to signal transmission.
Significant Decline in Reception Sensitivity: These fiber patch cords often fail to meet telecommunications-grade return loss and other testing standards. Although they may appear normal in routine testing, they are prone to packet loss in harsh environments or at slightly longer distances, seriously affecting network quality and stability.
Susceptibility to Insert Damage: Frequent insertion and removal operations can cause wear on the inner wall of the connector housing, affecting the coaxiality of optical devices and causing optical path deviation. This can lead to a series of problems such as decreased optical power, increased bit error rate, abnormal extinction ratio, ultimately resulting in increased network packet loss rate, frequent timeouts, system instability, and even prolonged network downtime in severe cases.
Significant Reduction in Service Life: Due to the use of non-standard components such as loose pieces, the service life of fiber patch cords is greatly reduced. This not only increases the cost of after-sales maintenance but also affects the stable operation of the entire network.
Failure to Pass 3D Inspection: These products often fail to meet telecommunications-grade standards, and therefore are often judged as unqualified in engineering projects. This directly results in engineering projects being unable to meet established standards due to fiber product quality issues, leading to significant losses for the project.

Therefore, when purchasing fiber patch cords, it is essential to choose products produced by reputable factories. These products typically adhere to stringent telecommunications-grade testing standards, ensuring reliable and stable product quality.



































































 Ann
Ann












