The fiber optic cable itself is not differentiated by gigabit or 10-gigabit speeds. When we refer to gigabit or 10-gigabit fiber in everyday life, we are actually talking about the transceivers (i.e., fiber optic ports). The primary distinctions between 10G and 1G fiber optic patch cables are made based on the following aspects:
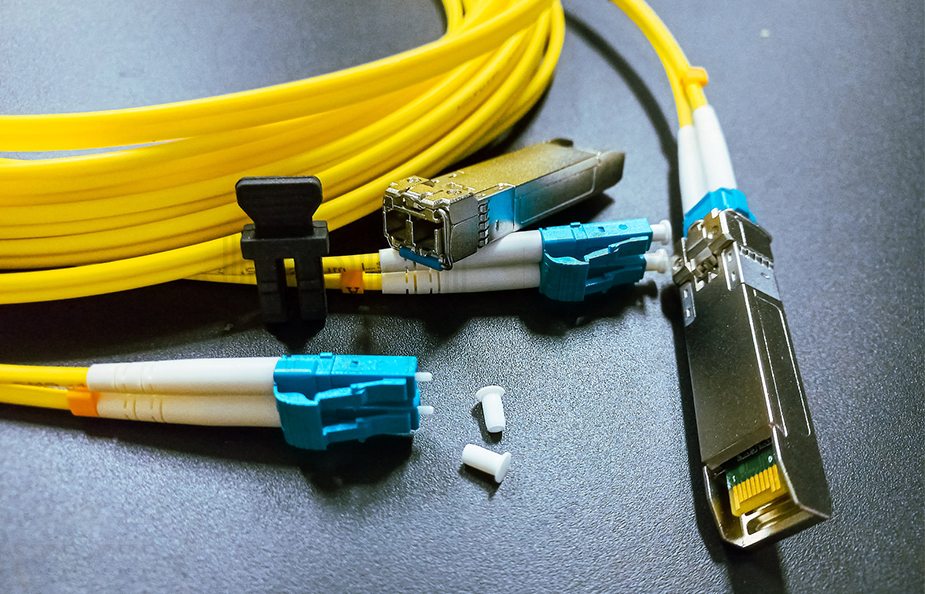

10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: Specifically designed for modern high-speed data centers and enterprise networks, these cables handle the demands of high-speed applications like big data and cloud computing with an impressive data transmission rate of 10 Gbps. They ensure smooth information flow and support efficient business operations.
1G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: Serving as the backbone of gigabit Ethernet transmission, these cables provide a stable data transmission rate of 1 Gbps. They meet the basic needs of daily network communication and data transfer, offering reliable support for small to medium-sized businesses, home networks, and campus networks.

10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: Specifically designed for modern high-speed data centers and enterprise networks, these cables handle the demands of high-speed applications like big data and cloud computing with an impressive data transmission rate of 10 Gbps. They ensure smooth information flow and support efficient business operations.

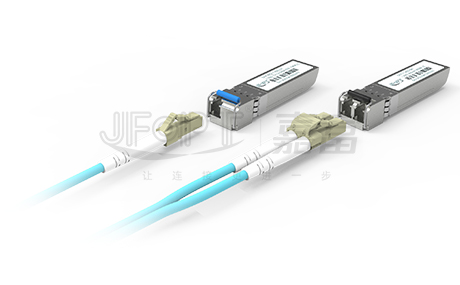
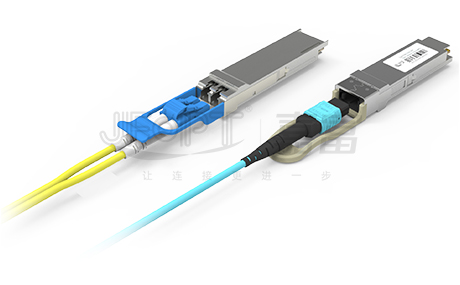
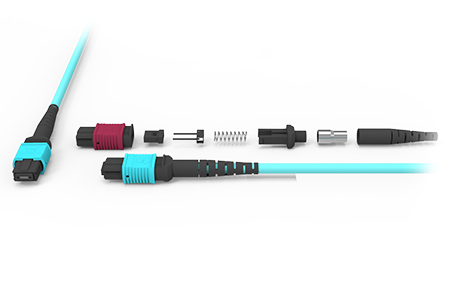
10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: To meet the stringent demands of high-speed data transmission, these cables commonly use high-density and highly reliable connector solutions such as LC, MPO, and specialized high-speed connectors like QSFP, QSFP+, and QSFP28. These connectors ensure signal transmission stability and efficiency while enhancing the integration and overall performance of network equipment through their compact design and optimized layout.
1G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: The choice of connectors is more flexible and diverse, compatible with various types of fiber optic connectors such as SC, LC, ST, and FC. Among them, the LC connector stands out due to its small size, excellent compatibility, and high-density characteristics, playing a significant role in the application of gigabit fiber optic patch cables. The widespread use of LC connectors further promotes the efficient deployment and stable operation of gigabit networks.
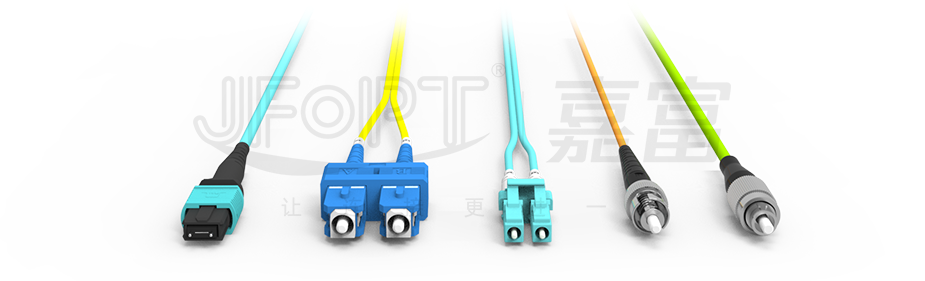

10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: These cables support a variety of core configurations in their design. They can be single-core to meet specific scenario requirements or multi-core (such as the common 8-core or 12-core MPO) to handle higher density data transmission challenges. This flexibility ensures that 10G fiber optic patch cables can adapt to various complex network environments, providing efficient and stable data transmission.
1G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: These cables also exhibit flexibility in core count configuration. They can have a single-core design, which is simple and efficient, or a multi-core configuration to meet the data transmission needs of specific scenarios. Whether single-core or multi-core, 1G fiber optic patch cables are dedicated to providing stable and reliable data transmission solutions.
10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: These cables have exceptional transmission capabilities, covering a range from a few hundred meters to several tens of kilometers. This wide adaptability is primarily due to the type of optical modules used and the carefully selected transmission medium. Whether for fast interconnections within data centers or long-distance communication across cities, 10G fiber optic patch cables provide stable and efficient data transmission solutions.
1G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: These cables are more focused on short to medium distance data transmission needs, with effective transmission distances typically ranging from a few hundred meters to several kilometers. This performance characteristic makes 1G fiber optic patch cables ideal for building local area networks, edge networks in data centers, and home broadband access. The exact transmission distance is influenced by factors such as the quality of the fiber used, the performance of the transmission equipment, and the network layout.
10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: To ensure their exceptional transmission performance, the fiber end faces undergo more precise grinding and polishing processes. This stringent requirement aims to eliminate any minor imperfections that could affect signal transmission, ensuring that optical signals can be transmitted efficiently and stably within the fiber. This meets the high standards of data integrity and transmission rates demanded by modern high-speed networks.
1G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: In comparison, the fiber end face treatment requirements for these cables are also standardized but generally less stringent. This is because 1G fiber optic patch cables are primarily used for more conventional network transmission needs. Their end face treatment balances basic performance requirements with cost-effectiveness and processing efficiency. Thus, while maintaining transmission stability, the end face treatment process for 1G fiber optic patch cables is relatively simpler and more efficient.
10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: To facilitate quick identification and selection by users, the outer packaging or connectors are usually clearly labeled with "10G" or "10 Gigabit." These markings not only intuitively display the product's performance characteristics but also ensure that users can quickly find the high-performance option that meets their needs among various fiber optic patch cables.
1G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: Following the same principle of easy identification, their packaging or connectors may be labeled with "1G" or "Gigabit." These clear and straightforward labels help users easily distinguish between fiber optic patch cables with different transmission rates, thereby meeting the data transmission needs of various network application scenarios.
10G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: As a leader in high-speed data transmission, these cables are widely used in various high-end network scenarios. This includes, but is not limited to, precise interconnections within data centers, high-speed connections between servers and high-end switches, and large-capacity data transmission between the core and distribution layers of enterprise networks. These scenarios demand high data transmission rates and stability, which 10G fiber optic patch cables excel at providing, offering robust support for the rapid development of modern networks.
1G Fiber Optic Patch Cables: With their moderate transmission rates and broad compatibility, these cables are ideal for the edge portions of enterprise networks and short-distance transmission scenarios. Whether connecting office computers, building small local area networks, or enabling short-distance high-speed communication between devices, 1G fiber optic patch cables deliver stable and reliable data transmission services to meet diverse user needs.
In summary, 10G and 1G fiber optic patch cables differ significantly in transmission rate, fiber type, connector type, fiber core count, transmission distance, fiber end face treatment, appearance markings, and application scenarios. When selecting the appropriate type of fiber optic patch cable, consider the interface type of the network equipment and the required transmission rate. Additionally, take into account the length of the fiber, quality standards, compatibility with existing network equipment, and cost-effectiveness.



































































 Ann
Ann












