With the continuous enrichment of network services, the requirement for network capacity is increasing, and Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) technology has emerged.
WDM is a communication technology that combines a series of optical signals with information but different wavelengths into a bundle and transmits them along a single fiber; the same technology is used at the receiving end to separate the optical signals of different wavelengths. This technology can transmit multiple signals on one fiber at the same time, and each signal is transmitted by a certain wavelength of light, and one wavelength is called a channel.
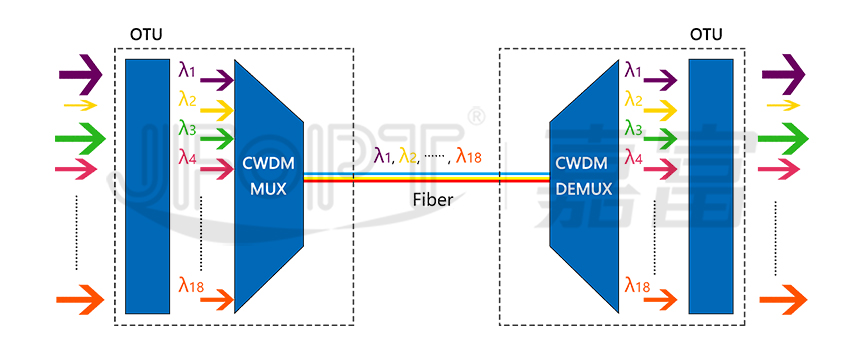
At present, there are two common WDM devices: CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer).
CWDM has many advantages such as low cost, low power consumption and small size. It is a low-cost WDM transmission technology for the access layer of the metropolitan area network.
DWDM takes the advantage of large bandwidth and low loss on single mode fiber, to use multiple wavelengths as carriers, allowing each carrier channel to transmit simultaneously in the fiber.
The difference between CWDM and DWDM:
According to the ITU-T standard, the working band of CWDM is defined as the range of 1270~1610nm (O, E, S, C, L bands), and 18 available wavelengths (18 channels) with a wavelength interval of 20 nm are recommended; The working bands of DWDM are defined as 1525-1565nm (C-band) and 1570-1610nm (L-band), the channel spacing is 1.6/1.8/0.4nm (200GHz/100GHz/50GHz), and the number of channels can be up to 40, 80 or even 160 channels. This is also why it is called CWDM and DWDM. Since the channels of DWDM are closely spaced, more information can be carried on the same optical fiber, so the bandwidth and capacity of DWDM are larger.
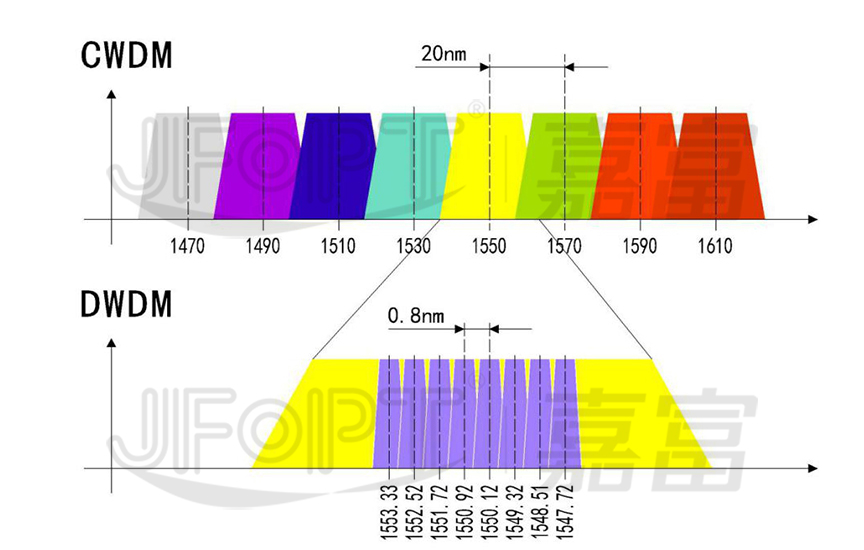
In the DWDM system, because the working wavelength is relatively dense, the wavelength interval is generally only a few nanometers to a few tenths of a nanometer. Therefore, it is required that the laser used in the DWDM system must have accurate wavelength, good stability and small wavelength shift. At present, it has to be high-cost cooled DFB lasers. For CWDM with 20nm spaced channels, the center wavelength shift should not exceed 6.5nm. Therefore, compared with the cooled DFB laser used in DWDM, the uncooled DFB laser used in CWDM has the advantages of small size, low power consumption and low cost.






































































 Ann
Ann












